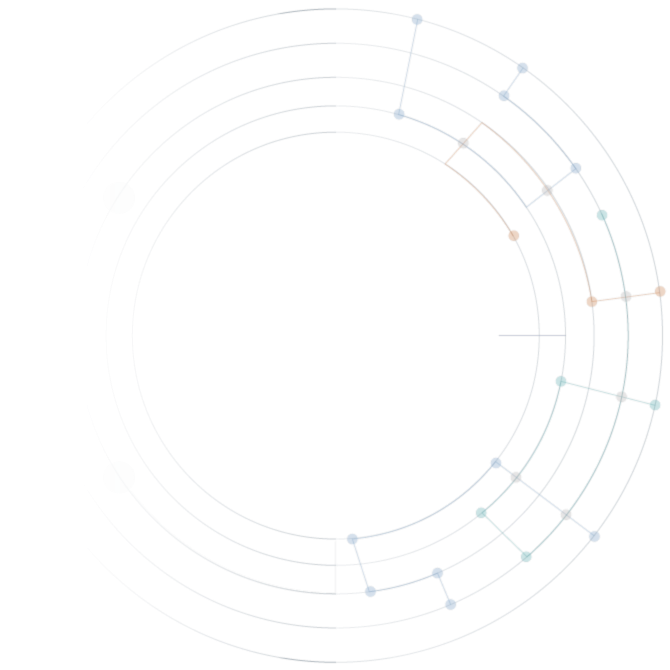
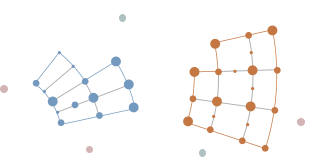
What is a work graph?
Description
A map of how teams experience digital work
Source
Derived from team-machine interactions
Value
What is hurting your teams and business outcomes?
Action
What can you do to improve business outcomes?
Largest human-made dataset: 300 trillion interactions every year

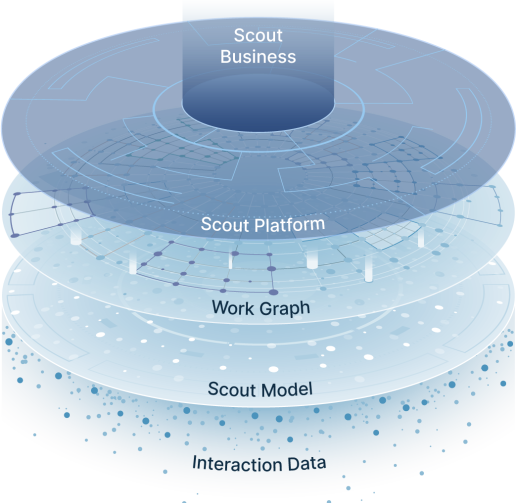
Interaction Data
AI Model
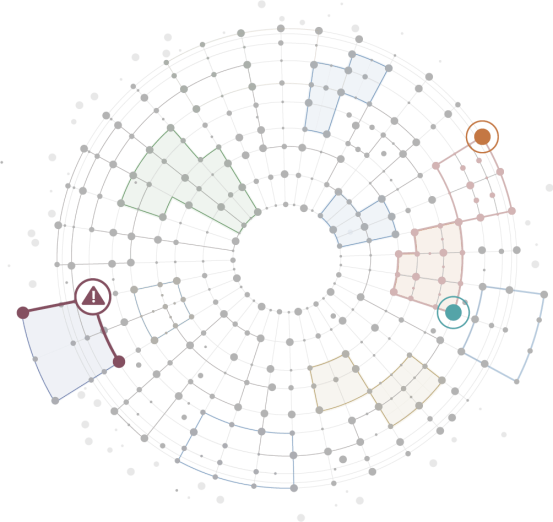
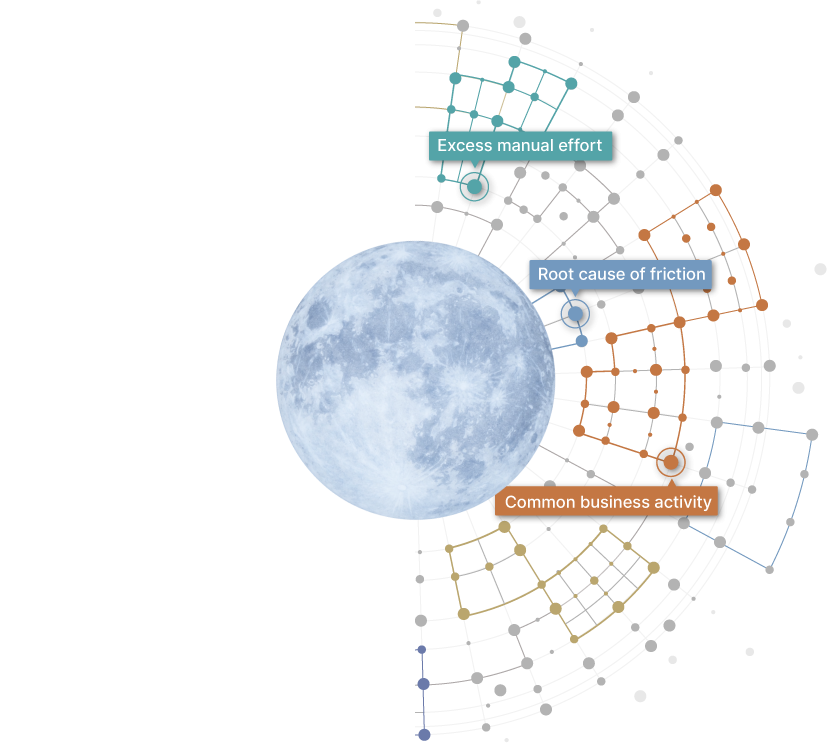
Root cause of friction
Disconnected debt arising from finance
systems are hurting the pace of revenue
recognition this quarter. Excess manual effort
Common business activity
Work Graph
The Scout stack
Scout leverages interaction data to build the work graph. Our products leverage the work graph to generate customer value.

Latest on the work graph
HFS Research Report
How Soroco Uses AI to Illuminate the 'Dark Side of the Moon'

Driving value from the work graph
Grow revenues
Optimize cost of operations
Manage risk & compliance
Deliver stellar experience (CX & EX)
Grow revenues
Optimize cost of operations
Deliver stellar experience (CX & EX)
Manage risk & compliance and ensure business continuity
Use case 1
Improve visibility for BCP for all work variations/ S4 Hana Migration
Privacy at the core
Data control in your hands
Scout only collects ‘opted-in’ data, respecting your consent.
Transparency is key – users can see accessed apps/URLs and pause data collection anytime
Transparency is key – users can see accessed apps/URLs and pause data collection anytime
Team-focused insights
Scout does not single out individuals. Anonymized user IDs protect privacy, ensuring dignity and anonymity
Privacy filters built-in
Scout scrubs sensitive info at the OS level, never reaching the servers. Zero risks of Personally Identifiable Information (PII) exposure. Your data, your privacy, our priority
Our thought leadership articles on HBR

Rooted in empathy

Focus on the team
(not the individual)
Empathy derived from how people experience work
Derived from human-machine interactions
Democratize change by empowering teams
Our thought leadership articles on HBR
Change the world with the work graph, one team at a time
We want to help every team in every company succeed
Every team will tap into their work graph and use it to help themselves